Keywords
Giant cell arteritis, subdural hematoma, arterial origin.
Abstract
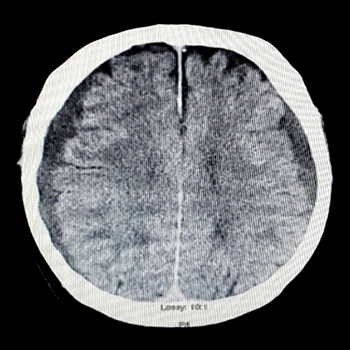
Giant cell arteritis or temporal arteritis is an inflammatory condition affecting medium to large sized vessels, particularly the cranial arteries. A 76-year-old man with no significant past medical history presented to the emergency department with a 3-week history of diffuse headaches associated with fever, loss of appetite, weight loss and general malaise. A CT scan of the brain showed bilateral shallow chronic low density subdural haematomas. A complete laboratory panel was unremarkable except for a raised erythrocyte sedimentation rate and elevated C-reactive protein. A transthoracic echocardiogram and CT scan of the body were unremarkable. MRI of the brain confirmed bilateral old subdural collections and showed marked vessel wall enhancement in the frontal branches of the left superficial temporal artery. A left temporal artery biopsy confirmed giant cell temporal arteritis. We speculate that a vasculitic process in the small subdural arteries may have contributed to our patient’s spontaneous subdural haematomas.
References
Views: 1205
HTML downloads: 437
PDF downloads: 403
Published:
2016-07-27
Issue:
Vol. 3 No. 5
(view)










