Keywords
Adult-onset Still’s disease, hypokalemia, intestinal pseudo-obstruction
Abstract
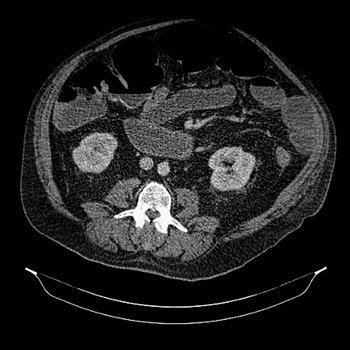
Adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) is a rare autoinflammatory disorder that can lead to a cytokine storm, causing a range of symptoms. Acute intestinal pseudo-obstruction is another rare condition that results in intestinal obstruction without anatomical cause. Although the two conditions are rarely reported together, we present the case of a 62-year-old male who developed acute intestinal pseudo-obstruction in the context of an AOSD flare. This led to severe hypokalaemia and a critical condition. Other symptoms included a high-spiking fever lasting for weeks, polyarthralgias and a typical salmon-coloured rash. After ruling out other potential causes, the patient was diagnosed with AOSD. Our findings suggest that the cytokine storm associated with this disease triggered the acute intestinal pseudo-obstruction and life-threatening hypokalaemia, establishing a causal relationship.
Only four other cases of AOSD complicated by intestinal pseudo-obstruction have been reported, and this is the first to present with life-threatening hypokalaemia. This case serves as a crucial reminder that, despite being a diagnosis of exclusion, Still’s disease should be considered as a potential cause of intestinal pseudo-obstruction, as prompt recognition and treatment of the underlying cause is crucial in managing this potentially life-threatening condition.
References
Views: 288
HTML downloads: 45
PDF downloads: 293
Published:
2023-05-30
Issue:
2023: Vol 10 No 6
(view)










