Keywords
COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2, toxic shock syndrome, Kawasaki disease, intensive care unit, IgG antibodies
Abstract
Paediatric inflammatory multisystem syndrome (PIMS) is associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients aged 19 years or below according to World Health Organization (WHO) criteria. The condition is characterised by fever, inflammation and organ dysfunction. PIMS mimics Kawasaki disease or toxic shock syndrome. As SARS-CoV-2 infection is a global pandemic, clinicians need to be aware of the conditions associated with it.
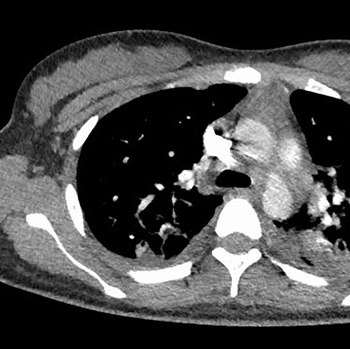
We present the case of 18-year-old woman who was admitted with multi-organ failure requiring admission to the intensive care unit. The differential diagnosis included toxic shock syndrome, Kawasaki disease and PIMS. The overall picture fit the criteria for PIMS but the patient had a negative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test for SARS-CoV-2, which presented additional diagnostic difficulties. As the PCR test was negative, IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 were measured to detect past infection and tested positive. The patient was diagnosed with PIMS as she met the WHO criteria after other differential diagnoses were excluded. She was successfully treated with methylprednisolone and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG).
References
Views: 460
HTML downloads: 51
PDF downloads: 296
Published:
2022-05-03
Issue:
2022: Vol 9 No 5
(view)










