Keywords
Metastatic prostate cancer, BRCA2 germline mutation, PARP inhibitor, olaparib, carboplatin, BRCA2-mutated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
Abstract
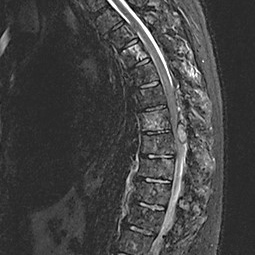
Prostate cancer is the second most frequent malignancy in men worldwide. Despite the improvement in survival achieved by increasingly early diagnosis and advances in treatment, it is still associated with high mortality. Because of its molecular heterogeneity, there is a need to identify genetic alterations in order to apply targeted therapies. Increasing evidence suggests that the PARP inhibitor olaparib could have a significant synthetic lethal effect in prostate cancer with homologous recombination defects, such as BRCA1/2 mutations. It is not yet known if, under these circumstances, platinum-based chemotherapy induces higher response rates in prostate cancer. We present the case of a patient with BRCA2-mutated metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer whose treatment sequence included carboplatin and olaparib.
References
Views: 646
HTML downloads: 114
PDF downloads: 482
Published:
2022-05-24
Issue:
2022: Vol 9 No 5
(view)










