Keywords
McKittrick-Wheelock syndrome, electrolyte imbalance, tubulovillous adenoma
Abstract
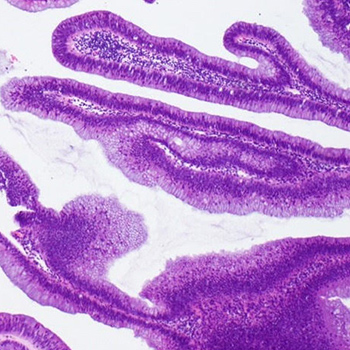
The authors present the case of a 79-year-old woman who presented with chronic secretory diarrhoea and severe electrolyte imbalance. A large rectal tubulovillous adenoma was discovered, leading to surgical resection of the tumour with complete resolution of the diarrhoea and electrolyte imbalance. The diagnosis of McKittrick-Wheelock syndrome was made.
We hope this case report will contribute to a greater awareness among health professionals about this clinical condition. A multidisciplinary approach is essential for the best outcome.
References
Views: 430
HTML downloads: 82
PDF downloads: 211
Published:
2022-03-24
Issue:
2022: Vol 9 No 3
(view)










