Keywords
Hepatitis, hepatic failure, immunotherapy, renal carcinoma
Abstract
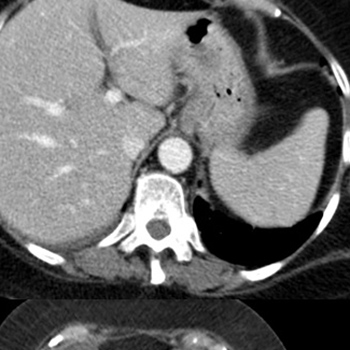
Hepatic dysfunction, in the absence of liver metastases, occurs in 10–15% of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) patients, while immune hepatitis due to anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD1 administration affects about 3–9% and 0.7–1.8% of treated patients, respectively. Liver toxicity following combination therapy (anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD1) is seen in 29% of patients overall and grade 3–4 toxicity in 14% of patients.
Stauffer’s syndrome is a rare para-neoplastic phenomenon associated with RCC and characterized by abnormal liver function tests, hepato-splenomegaly and histological changes consistent with non-specific hepatitis. We describe a case of RCC treated with anti-CTLA4 and anti-PD1 therapy resulting in immediate liver toxicity and death after 2 months of progressive hepatic impairment. We hypothesize that high IL-6 levels due to Stauffer’s syndrome might have contributed to immune-related hepatic failure.
References
Views: 714
HTML downloads: 124
PDF downloads: 329
Published:
2021-06-17
Issue:
2021: Vol 8 No 6
(view)










