Keywords
Idiopathic intracranial hypertension, diplopia, monocular diplopia, papilloedema
Abstract
Background: Diplopia is the double vision of a single object, and can be binocular or monocular. Binocular diplopia is caused by the misalignment of the visual axes, with images falling on the fovea of the fixating eye and on the extra-foveal retina of the non-fixating eye, as a consequence of both neurological (i.e., oculomotor nerve palsies, ocular myopathies, neuromuscular junction disorders) and ophthalmic disorders (i.e., decompensation of a pre-existing strabismus). In contrast, monocular diplopia is generally explained by intraocular pathology (i.e., refractive errors, ocular media abnormalities, dry eyes), causing the image of a single object to fall, at the same time, on the fovea and on the extra-foveal retina of the same eye.
Methods: We report the case of a 22-year-old woman presenting with acute-onset monocular diplopia.
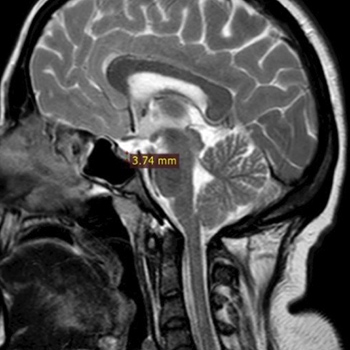
Results: The diagnosis of idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) was based on the presence of papilloedema and elevated cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) pressure. Monocular diplopia resolved after CSF subtraction.
Conclusions: We describe a case of monocular diplopia as a presenting symptom of IIH, and discuss diagnostic issues of this possibly underestimated symptom in neurology clinical practice. Careful ophthalmic and neuro-ophthalmic examination can identify clinical features of diplopia, and drive diagnosis and treatment.
References
Views: 925
HTML downloads: 255
PDF downloads: 506
Published:
2021-05-04
Issue:
2021: Vol 8 No 5
(view)










