Keywords
Chronic renal failure, hyperkalaemia, sodium polystyrene sulfonate, iatrogenic ischaemic colitis
Abstract
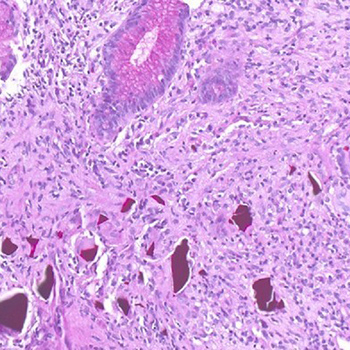
Case description: A 64-year-old patient with chronic renal failure and persistent hyperkalaemia not corrected by dialysis, was prescribed sodium polystyrene sulfonate (SPS) at a low dose (30 g/day for 2 days a week during the long interdialytic interval). After 3 months of therapy, the patient developed intense abdominal pain with non-specific colitis identified with a colonoscopy. In addition, the biopsy specimens showed rhomboid SPS crystals in the intestinal mucosa. Fourteen months after discontinuing therapy, the patient again presented with colitis and persistent biopsy finding of SPS crystals. The patient died a few months later due to intestinal infarction.
Discussion and conclusion: SPS is a cation exchange resin used to treat hyperkalaemia resistant to dialysis, but may cause inflammation and ischaemia of the colon. In our patient, a short 3-month course of low-dose SPS therapy (without sorbitol, which is used to counter iatrogenic constipation caused by SPS) induced relapsing colitis, which was followed by massive intestinal infarction a few months later. In light of frequent reports of its enterotoxic effects, SPS should be replaced with the new potassium chelators (patiromer and sodium zirconium cyclosilicate).
References
Views: 937
HTML downloads: 74
PDF downloads: 408
Published:
2021-01-19
Issue:
2021: Vol 8 No 1
(view)










