Keywords
Haematology/oncology, non-small-cell lung cancer, leucocytosis, eosinophilia
Abstract
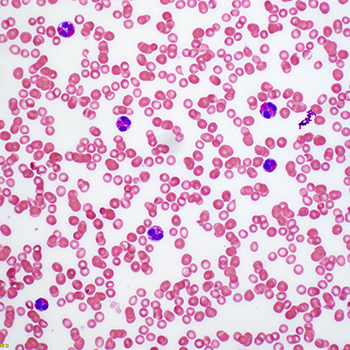
Significant leucocytosis in the setting of an underlying malignancy may be attributed to several causes and is not uncommon; however, extreme leucocytosis (>50×109 cells/l) and hypereosinophilia is less common and may represent a paraneoplastic syndrome. The underlying mechanism is thought to be bone marrow stimulation by tumour-produced cytokines, most notably interleukin-5 (IL-5) and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF). This paraneoplastic syndrome is likely reflective of extensive disease and dissemination, and options for treatment are limited but include tumour resection, corticosteroids and hydroxyurea. In this report, we discuss an unusual case of known stage III lung adenocarcinoma presenting with an ischaemic stroke and extreme leucocytosis and hypereosinophilia.
References