Keywords
Ciprofloxacin, hepatitis, adverse drug reaction
Abstract
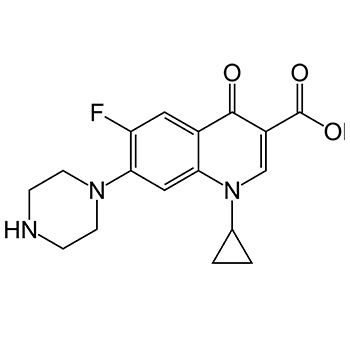
Fatal hepatotoxicity associated with ciprofloxacin is extremely rare. This is the second fully investigated case of fulminant hepatotoxicity due to ciprofloxacin in a male patient previously ciprofloxacin tolerant. The patient’s medical history included stable Waldenstrom’s macroglobulinaemia, inguinal hernia repair, prostate cancer (radiotherapy in 2006) and idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Extensive investigation for progressive liver failure confirmed drug-induced liver injury.
References