Keywords
Hand-foot-mouth disease, enterovirus, viral illness, exanthematous fever
Abstract
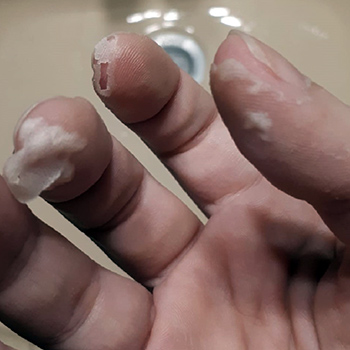
Non-polio enteroviruses are ubiquitous viruses responsible for a wide spectrum of disease in people of all ages, although infection and illness disproportionately affect infants and young children. Hand-foot-mouth disease (HFMD) is an enteroviral clinical syndrome most frequently caused by coxsackievirus-A16 and enterovirus-A71. Since 2008, a novel coxsackievirus-A6 genotype has been associated with more severe HFMD in both children and adults, presenting with a unique constellation of findings, and whose prevalence has been increasing over the last few years. In this case report, an atypical clinical picture of confirmed enterovirus HFMD is described in an immunocompetent adult, with exuberant clinical findings, clinically consistent with coxsackievirus-A6 infection. This case report highlights the importance of awareness of the clinical presentation of this increasingly common infection in adults.
References
Views: 2054
HTML downloads: 6085
PDF downloads: 669
Published:
2020-04-13
Issue:
2020: Vol 7 No 7
(view)










