Keywords
Bilateral craniectomy, decompressive craniectomy, malignant cerebral venous thrombosis
Abstract
Introduction: Despite the extremely favourable prognosis of patients with cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT), death occurs in 10–15% of patients. In severe cases of malignant CVT with supratentorial haemorrhagic lesions, cerebral oedema and brain herniation, decompressive surgery may be the only life-saving treatment.
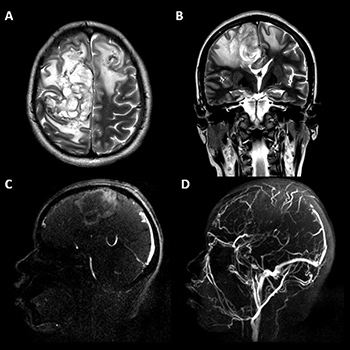
Patient and methods: We present the case of a puerperal young woman with progressive headache, seizures and decreased alertness. Thrombosis of the entire superior sagittal sinus with bifrontal venous infarcts and midline shift was confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging with venography sequencing. Despite medical treatment with anticoagulation, progressive neurological deterioration was observed, so bilateral, frontal decompressive craniectomy was performed.
Results: At the 6-month follow-up, we observed partial functional recovery with a modified Rankin score of 3.
Discussion: Bilateral decompressive craniectomy may be a life-saving therapeutic option when medical therapy fails and there are clinical and radiological features of progression in both cerebral hemispheres.
References
Views: 1555
HTML downloads: 99
PDF downloads: 468
Published:
2020-04-21
Issue:
2020: Vol 7 No 7
(view)










