Keywords
Nitrofurantoin, pulmonary toxicity, drug-induced lung toxicity, organising pneumonia
Abstract
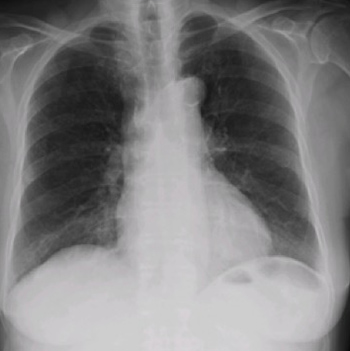
Nitrofurantoin-induced diffuse lung toxicity is well documented in the literature but is often misdiagnosed. We describe an 82-year-old female medicated with nitrofurantoin for the previous 2 years who was admitted for dyspnoea, dry cough and fatigue for 4 months. She was febrile and tachypnoeic and she presented with bilateral basal crackles, hypoxaemic respiratory failure and slightly elevated C-reactive protein levels. A chest radiograph showed bilateral air-space consolidation and interstitial infiltrates and the high-resolution computed tomography scan was evocative of a perilobular pattern of organising pneumonia (OP). Due to the clinical–radiological context, she was diagnosed with a presumable nitrofurantoin-induced OP. She was started on prednisolone 60 mg daily with a progressive improvement. It is important that clinicians are aware of the spectrum of side effects associated with nitrofurantoin so as to monitor patients.
References