Keywords
Disseminated intravascular coagulation, lung cancer, intracerebral bleeding
Abstract
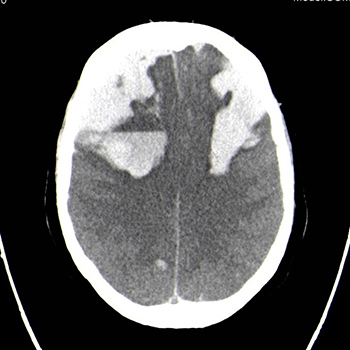
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is an acquired syndrome characterized by the widespread activation of coagulation. It can present as an acute life-threatening emergency or as a chronic process. Mortality is highly dependent on the reversibility of the aetiology and degree of coagulation impairment, so treatment of the underlying cause is vital. The authors present the case of a 57-year-old man whose inaugural presentation of lung cancer was chronic DIC, characterized by three thrombotic events, followed by acute DIC, culminating in death. Metastatic lung cancer was diagnosed only after death.
References
Views: 1120
HTML downloads: 289
PDF downloads: 557
Published:
2019-06-03
Issue:
Vol 6 No 6
(view)










