Keywords
Giant cell arteritis, intracranial stenosis, ischemic stroke, vascular imaging, endovascular treatment
Abstract
Giant cell arteritis (GCA) may manifest with aggressive intracranial stenosis resistant to medical therapy, and patients may develop refractory neurologic deficits and cerebral infarcts, making GCA a life-threatening condition.
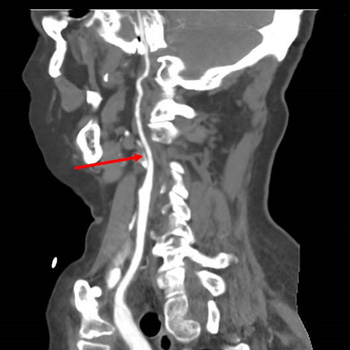
We report the case of a 68-year-old woman recently diagnosed with GCA, medicated with prednisolone 60 mg daily. Two weeks later, the patient was admitted to our Stroke Unit after a sudden episode of global aphasia. Magnetic resonance angiography showed two recent ischaemic lesions, besides an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 17 mm/hour. A cerebral angiography revealed bilateral stenosis and dilation in the petrous, cavernous and supraclinoid segments of internal carotid arteries (ICA). The patient was started on intravenous methylprednisolone pulses (250 mg daily for five days). Computed tomography (CT) angiography and Doppler ultrasound showed severe vascular disease affecting multiple territories, without significant intracranial involvement. The hypothesis of GCA with extracranial vasculitic involvement was considered as the aetiology of ischaemic cerebral infarctions in multiple territories and, given the severity of the disease, it was decided to add tocilizumab. Despite this, the patient evolved with significant worsening neurological deficits and a CT scan confirmed the presence of new vascular events. Endovascular treatment (EVT) with balloon angioplasty was conducted on both ICAs, with improved calibre and downstream filling. After that, the patient presented sustained clinical improvement, without recurrence of any ischaemic events at the one-year follow-up.
This clinical case stands out for the importance of EVT as an effective therapy in patients with medically refractory GCA with symptomatic intracranial stenosis, improving their prognosis.
References
Views: 265
HTML downloads: 11
PDF downloads: 190
Published:
2024-02-08
Issue:
2024: Vol 11 No 3
(view)










