Keywords
COVID-19, Valsalva, pneumothorax
Abstract
Background: Until now, only a few cases of Valsalva-induced barotraumas (pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum and subcutaneous emphysema) have been described, and none of them among COVID-19 patients.
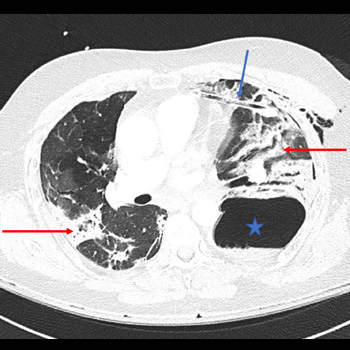
Case description: A man in his 50s was admitted for SARS-CoV-2-related acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Initial evolution was favourable with non-invasive ventilatory support, high-flow oxygen nasal cannula and the best supportive drugs available at the time. During the Valsalva manoeuvre while defecating, the patient reported sudden chest pain and showed a new acute hypoxemic respiratory failure due to a pneumothorax. It led to multiple complications (pulmonary embolism, haemoptysis, and cardiac arrest), and despite the best supportive care, led to the patient's death.
Discussion: The Valsalva manoeuvre can be an overlooked cause of pneumothorax in patients with COVID-19. Predisposition to barotrauma in COVID-19 patients could be explained by several factors, including the extensive use of non-invasive and invasive ventilation during the pandemic, and the histological changes observed in the lungs of those infected with COVID-19.
Conclusion: We report the first description of a Valsalva-induced barotrauma in a COVID-19 infection. We emphasise the importance of treating constipation particularly in severe COVID-19 cases, to prevent complications such as barotrauma.
References
Views: 240
HTML downloads: 16
PDF downloads: 168
Published:
2024-02-28
Issue:
2024: Vol 11 No 3
(view)










