Keywords
Morgagni hernia, diaphfragmatic hernia, hernia repair, Morgagni hernia in adult
Abstract
Background: Congenital diaphragmatic hernias are rare congenital defects resulting in abdominal organ protrusion into the thoracic cavity; they mainly present with pulmonary or gastrointestinal symptoms. Although congenital and discovered in utero or in early childhood, they can be asymptomatic for a long time and even remain asymptomatic despite the growing hernia sac dimensions and the hernia sac contents.
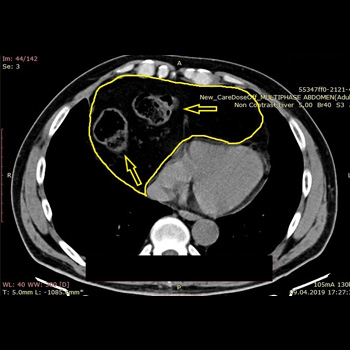
Case description: We present a case of a 58-year-old patient with incidentally diagnosed Morgagni hernia during the COVID-19 pandemic following a computerised tomography (CT) scan of the chest. He presented without any symptoms related to the existence of the hernia. Another CT scan was performed 20 months after the initial diagnosis to evaluate the progression of the hernia. The patient refused the offered surgery due to the absence of symptoms.
Discussion: A Morgagni hernia is usually discovered during pregnancy or in early childhood, but sometimes can be asymptomatic for years. Main symptoms originate from the respiratory and gastrointestinal system.
Conclusion: Due to the refusal of surgery, we were able to follow the CT scan enlargement progression of patients’ hernia over a 20-month period.
References