Keywords
pituitary adenoma, thyrotoxicosis, hyperthyroidism, thyrotropin, neurosurgery
Abstract
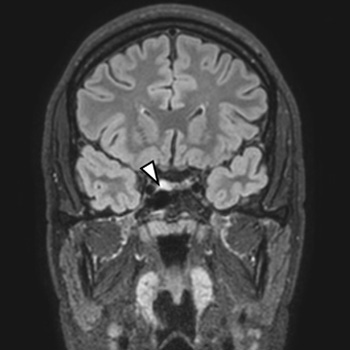
We report a case of a 19-year-old young male presenting with thyrotoxicosis with inappropriately elevated TSH. Magnetic resonance imaging revealed a pituitary adenoma (8.2 x 9.7 mm), TRH stimulation test showed abnormal blunted TSH response, and serum glycoprotein hormone alpha-sub-unit was elevated. He had no family history of thyroid disease and TR-beta genetic testing excluded resistance to thyroid hormone action. The diagnosis of thyrotropin-secreting pituitary adenoma (TSHoma) was presumed and long-acting somatostatin analogue was promptly initiated. After two months of octreotide treatment, serum TSH and FT3 returned to within normal ranges. Tumour resection by transsphenoidal surgery was performed and, ten days after surgery, clinical hypothyroidism was achieved, despite detectable TSH levels (TSH 1.02 µU/ml[RR 0.27-4.2]). Although the patient remained euthyroid for the following three years, there was a gradual biochemical elevation in the levels of TSH, FT4, and FT3 over time, reaching serum values above the normal limit in the third year after surgery. Imaging did not show neoplasm recurrence at this point. After two years, the patient presented with clinical manifestations of re-onset thyrotoxicosis, with MRI revealing a T2 hypersignal oval area compatible with a pituitary adenoma. Adenectomy was performed. Histopathological and immunohistochemical analyses revealed a pituitary adenoma with transcription factor PIT1 expression and positivity for TSH and PRL. TSHoma treatment may not be always effective in the first therapeutic approach and recurrences are a possibility, making follow-up essential. The present case highlights the heterogeneity of post-treatment cure criteria and their limitations.
References
Views: 362
HTML downloads: 68
PDF downloads: 337
Published:
2023-05-15
Issue:
2023: Vol 10 No 6
(view)










